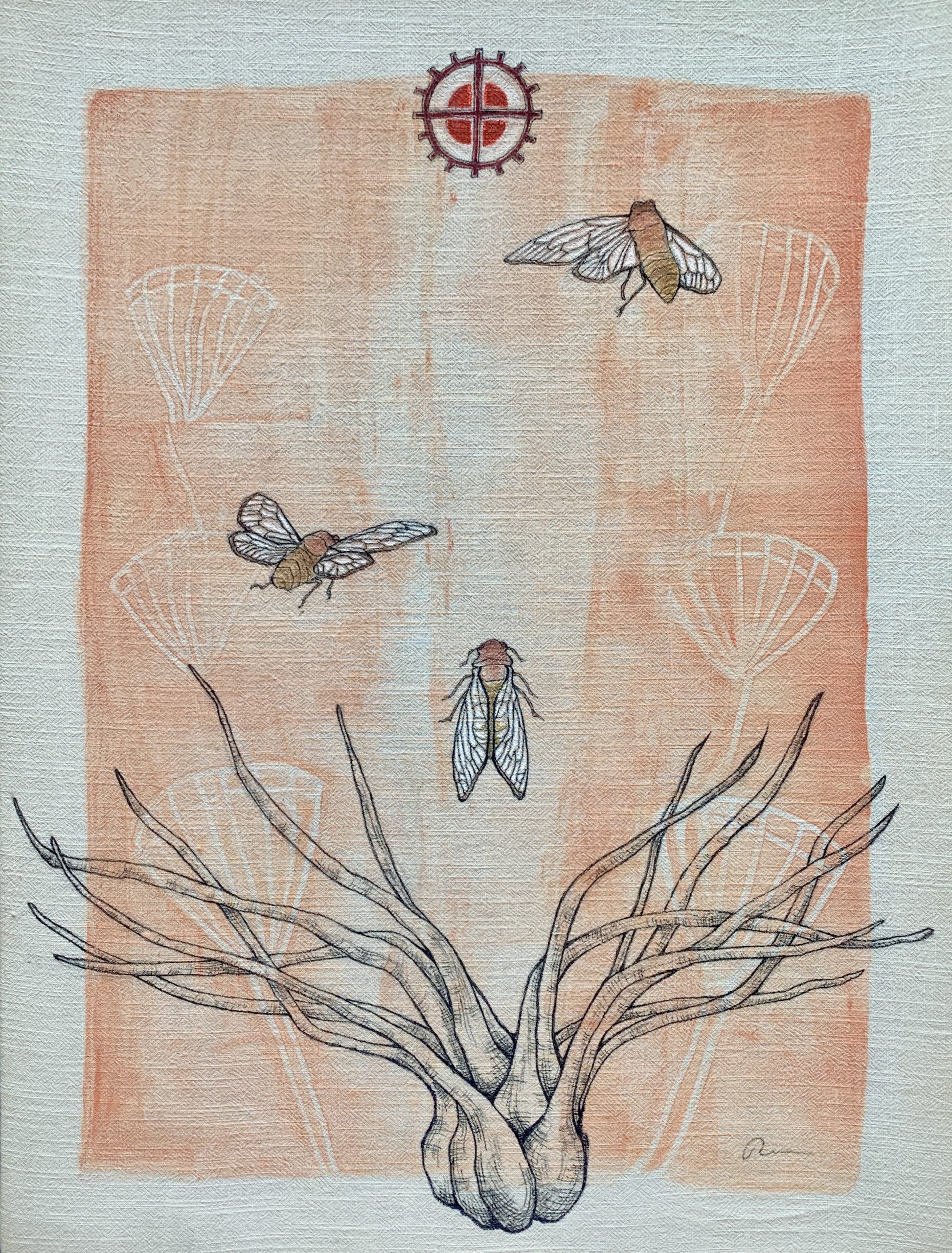

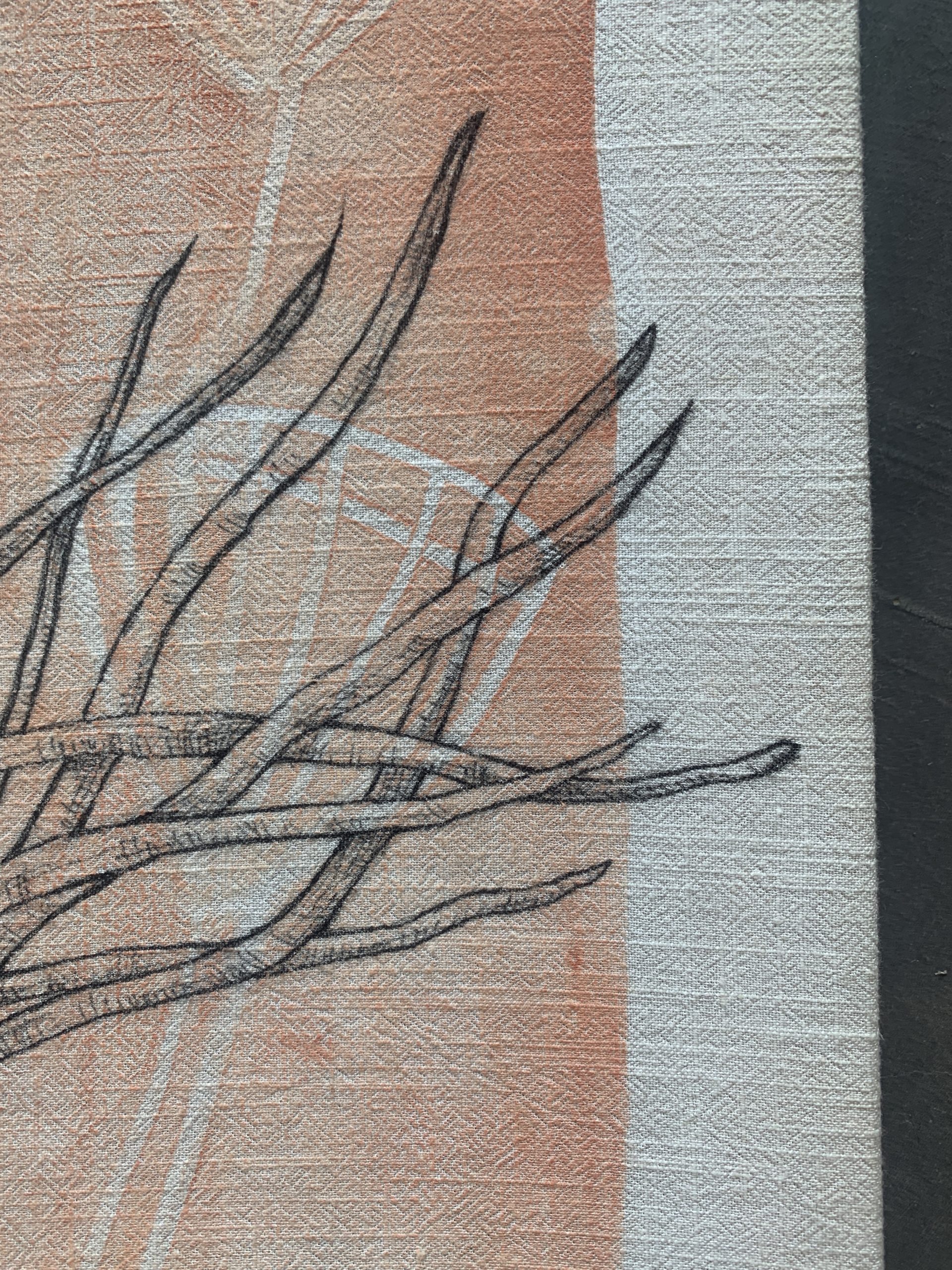
Isoetes melanospora/Black-spored Quillwort, or Merlin’s grass, is an endangered aquatic lycophyte native to Georgia and South Carolina, first “discovered” in 1877. This plant grows in shallow, temporary pools on top of granite outcrops, in only 2 cm of soil. Following its original discovery, the number of sites where this species can be found has dropped drastically due to human activity such as quarrying, trash dumping and trampling. It is mostly threatened because Georgia’s “flatrocks” are being quarried at an alarming pace, making the state the world’s largest producer of granite building stone. This granite is used for kitchen countertops and other building materials. Over 40% of historic quillwort populations have already been lost to quarrying. Georgia’s law does not protect this plant against habitat destruction, putting profit-driven quarrying corporations in front of plant protection efforts.
Some efforts are being made to build alternative homes for these plants, in newly-constructed granite bed pools.

To support conservation and research efforts for this endangered plant donate to the Emory University Herbarium Rare Plant Collection:
•(404) 727-7065
•cquave@emory.edu
Emory University Herbarium Project
@emory.herbarium
.
Contact the US Fish and Wildlife Service in Georgia to learn more about the 1993 Fish and the “Wildlife Service Recovery Plan for Three Granite Outcrop Plant Species”:
U. S. Fish and Wildlife Service
Regional Office, Division of Endangered Species
1875 Century Blvd., Suite 200
Atlanta, Georgia 30345
US Fish and Wildlife Service, Division of Endangered Species